Kia Optima: Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS) / Surround View Monitor (SVM)
Components and components location
| Surround View Monitor (SVM) |
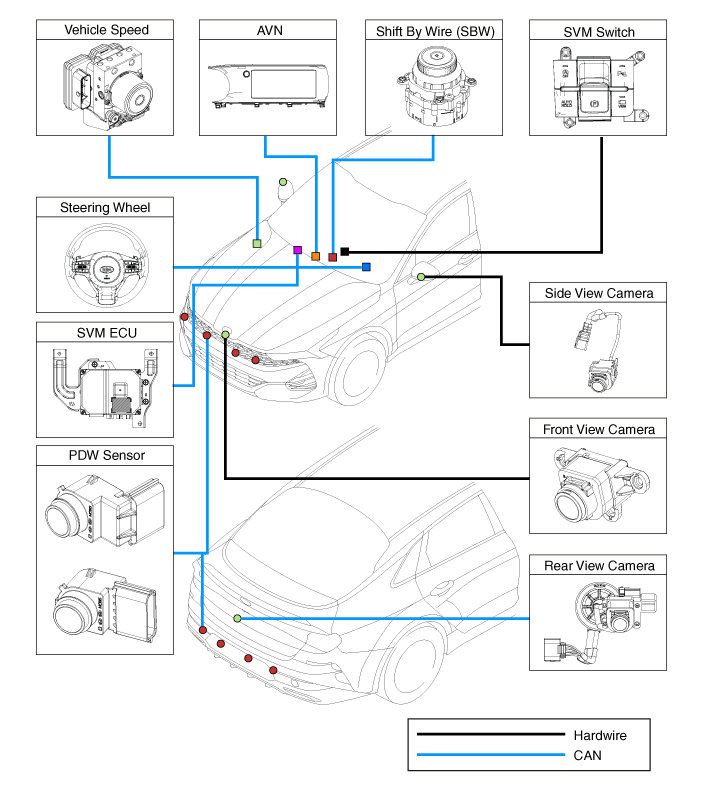
|
1) SVM unit basically transmits data via C-CAN only.
|
| • |
Steering wheel angle sensor : C-CAN
|
| • |
Vehicle speed sensor : C-CAN
|
|
2) It functions as a CGW (Central gateway) of C-CAN ↔ B-CAN,
P-CAN, MM-CAN in ICU.
e.g. The signal of unit using B-CAN, P-CAN, MM-CAN is transmitted
after converting to C-CAN in cluster.
|
| • |
Transmission : P-CAN (TCU)
|
| • |
PDW sensor : B-CAN (IBU)
|
|
| – |
Steering Wheel Sensor : The steering wheel angle is transmitted to the
SVM unit through the C-CAN communication line for display of the rear view
and steering assisted parking guideline.
|
| – |
Transmission : The shift lever position is transmitted to the SVM to
determine its operation.
|
| – |
Front/Rear PDW : An alarm screen to display obstacles appears on the
omnidirectional monitor that receives data from the parking distance warning
(PDW) sensor on the front and rear.
|
| – |
SVM Unit : It controls the overall operations for video signal processing/input/output,
vehicle communication (CAN), and SVM system.
|
| – |
SVM Switch : The SVM switch signals are input to determine whether or
not to provide images in forward display mode.
|
| – |
Vehicle Speed Sensor : The vehicle speed is transmitted to the SVM to
check the SVM operation condition.
|
| – |
Camera (4 unit) : Each unit is mounted on the front, rear, and left/right
outside mirrors to capture images from the surroundings and to transmit
them to the SVM unit.
|
| – |
AVN Monitor : It provides the driver with the output image from the SVM
unit through the monitor of the AVN (Audio, Video and Navigation system)
head unit.
|
Description and operation
Surround View Monitor (SVM) allows video monitoring of 360 degrees around the
vehicle. The system consists of 4 ultra optical cameras mounted around the vehicle
(front, both sides and rear).
The video images from these cameras are applied with distortion compensation,
time point conversion, and video merging technologies to provide sky-view image
of the vehicle's surrounding area, as well as various other view modes.
The SVM System provides video feed of the vehicle's surrounding area while parking
or during low speed driving to the driver to enhance safety and driver's convenience.
Also, it features steering wheel synchronized guide line indication, front and
rear object warning, and A/S (including In-Line) tolerance compensation.
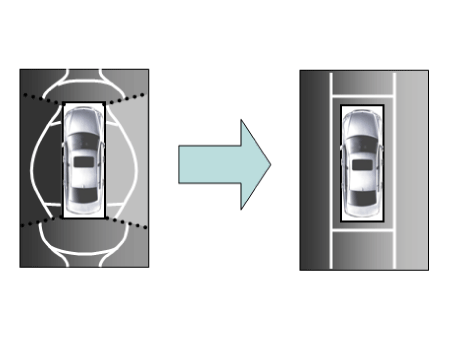
This system displays the video images from ultra optical cameras mounted on 4
sides of the vehicle, on the Head Unit Screen. It shows 360 degrees sky-view image
of the vehicle's arounding area, as well as various other view modes.
Blind-spot View Monitor
(BVM)
Blind-spot View Monitor (BVM) is a driving safety system that helps provide a
more comprehensive views on areas which is not usually visible by the side mirrors
when the vehicle tries to change the lane.
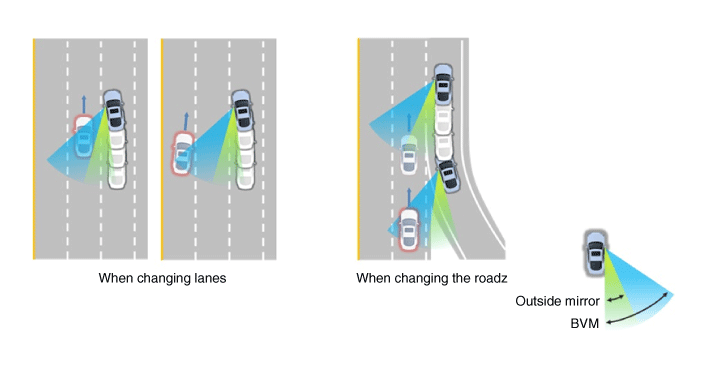
The BVM system provides a driver a more comprehensive view which is not usually
visible by the side mirrors in certain situations like swithing drive lanes. The
system helps to avoid any blind spot mishaps.
| – |
The rear side view is displayed in the cluster screen when the turning
lights are in operation as the light switch goes up and down by the driver.
|
| – |
The SVM also provides an edited view of the left side/ right side without
adding more cameras.
|
| – |
It helps minimize the distraction of the driver by displaying the rear
side view that is usually hard to see.
|
| • |
The video will be played even though the side mirrors are folded.
But it does not provide a proper view of the surroundings.
|
| • |
The video quality may be lower than the SVM video as the size
of the original image has to be adjusted to fit the cluster.
|
| • |
The screen may temporarily fades out with changes in light conditions
during daytime or with a sunrise or a sunset. Or when the car enters
the tunnel.
|
| • |
The view of the surrounding objects provided by the system may
look far away than views that are obtained by the side mirrors.
|
| • |
The brightness of the rear side video may change due to a mode
switching delay of the SVM/BVM.
|
|
| 1. |
Display Surrounding Area of Vehicle in Video
| • |
The surrounding area video display function displays 360 degrees
video image captured from four cameras on the Head Unit Screen while
the vehicle is moving at low speed or reversing. The SVM System
displays total 8 video modes for displaying surrounding video based
on the vehicle driving state and the driver's selection.
|
|
| 2. |
Guide Line Indication & Steering Wheel Synchronized Feature
| • |
The Guide Line Indication & Steering Wheel Synchronized Feature
is the function that assists the driver in parking by synchronizing
the steering wheel with the rear view video display marked with
a guide line to help anticipate the direction of the reversing vehicle.
|
|
| 3. |
Front/Rear Object Warning (Obstacle Detection Feature)
| • |
The system receives obstacle warning signal from the PDW sensors
mounted on the front/rear of the vehicle and displays the obstacle
location on the AVN Head Unit Screen.
|
|
| 4. |
Tolerance Compensation (including A/S)
| • |
Manual Tolerance Compensation Software is embedded in the SVM
ECM to compensate the SVM deviation that may occur due to assembly
line installation tolerance. You must first setup proper work environment
in order to perform correct tolerance compensation.
|
|
| 5. |
Rear-view display while driving
| • |
The function displays the rear view even in N or D upon request
of the driver. It provides an optimized image under driving condition
unlike parking mode.
|
|
No.
|
Main Features
|
Detailed Description
|
Notes
|
1
|
8 Display View Modes
|
| • |
4 Front & 4 Rear Display View Modes
|
|
Merged Video Display of 8 Modes
|
2
|
Front Assist Mode Selection Feature
|
| • |
Display only the Front Mode by using the Front Mode Selection
Switch
|
|
Same as the PDW SVM Switch
|
3
|
Rear Steering Synchronized Parking Guide Line Display
|
| • |
Displays Parking Guide Line by synchronizing with the steering
wheel when going reverse.
|
|
Display over the Rear Video
|
4
|
PDW Obstacle Indication
|
| • |
Display obstacle warning from rear and front PDW
|
|
Display both on the Cluster and the Head Unit
|
5
|
User Setting Option
|
| • |
Select Steering Wheel Synchronized Guide Line Indication
|
| • |
Select Front/Rear Obstacle Indication
|
| • |
Select Initial Front/Rear View Screen
|
|
Provides additional screen settings
|
6
|
Assembly Line & A/S Tolerance Compensation Feature
|
| • |
Compensation - Tolerance Compensation for camera installation
deviation and assembly line tolerance is required
|
|
Compensation function recognition logic applied
|
SVM Mode Entry Conditions
The vehicle information is accessed regularly, even after entering SVM mode.
When the conditions are met, conversion from front mode to rear mode is available,
and vice versa.
When the mode is converted, the view displayed on the screen can be the initial
view or the previous view depending on the conditions.
If the mode for conversion is the initial entry, the default view is selected
based on the front or rear. If a continuous front-rear conversion mode occurs as
forward and backward movement are repeated for parking, the previous view is recalled
and displayed.
| – |
Initial Entry : When the rear and front view modes in SVM mode are displayed
on the screen for the first time.
|
| – |
Re-entry: When switching from SVM mode to another mode, without turning
off SVM, and returning to the previous mode.
(e.g. Rear → Front → Rear: Re-enter rear mode / Front → Rear → Front:
Re-enter front mode)
|
Switch mode
|
Vehicle speed
|
Gear
|
SVM Switch
|
Display view
|
Rear → Front
|
Below 10 MPH (15 km/h)
|
"R" Range or "P" Range excluded
|
ON
|
Initial Entry: Front view set in the initial view mode option
|
Re-entry: The last view mode displayed in the previous front mode
|
Front → Rear
|
Irrelevant
|
Reverse Gear
|
Irrelevant
|
Initial Entry: Rear view set in the initial view mode option
|
Re-entry: The last view mode displayed in the previous rear mode
|
SVM Mode Disengagement
If the conditions below are satisfied while in SVM mode, the SVM is turned OFF
and no video is displayed.
OFF Mode
|
Vehicle speed
|
Gear
|
SVM Switch
|
Notes
|
Front mode
|
Over 10 MPH (15 km/h)
|
"R" Range or "P" Range
|
OFF
|
If any of the three conditions is satisfied
|
Rear mode
|
Irrelevant
|
Except "R" gear
|
Irrelevant
|
If any of the two conditions is satisfied
|
SVM Options
Considering the user's convenience, the SVM provides three options for the user
to select from.
The window for changing options (parking guide settings) is displayed on the
AVN. Only the changed options are forwarded to the SVM ECU through M_CAN.
These three options are applied as soon as they are selected by the user. Based
on the conditions, the initial views displayed are as follows.
Option
|
Function
|
Default setting
|
Guideline steering interlocking
|
Interlocks with steering to display the driving direction of the vehicle
during parking.
|
Classification code
|
Close range warning indicator
|
Indicates front and rear obstacle detection
|
Classification code
|
Initial view mode setting
|
Default view displayed when entering SVM mode
|
Front + Around view
|
Rear + Around view
|
Operations for Guideline
Steering Interlocking Indications
The guideline for steering interlocking trace is indicated by using the value
of steering wheel angle periodically received by SVM ECU via C-CAN.
A combination of the rear area that displays of the rear mode (two-split mode)
and the expected car movement trace displayed on the wide view is displayed.
| 1. |
View modes for guideline steering interlocking indications
Mode
|
View
|
Notes
|
Rear
|
Rear wide view + Surround View
|

|
Rear top view + Surround View
|

|
Rear side view + Surround View
|

|
|
| 2. |
Specifications for guideline steering interlocking trace lines
Description
|
Number
|
Distance
|
Color
|
Steering wheel interlocking trace lines
|
①
|
19.6 in. (0.5 m)
|
Red
|
②
|
39.3 in. (1.0 m)
|
Yellow
|
③
|
118.1 in. (3.0 m)
|
Yellow
|
④
|
Vehicle left side end + 11.8 in. (0.3 m)
|
Red + Yellow
|
⑤
|
Vehicle right side end + 11.8 in. (0.3 m)
|
Red + Yellow
|
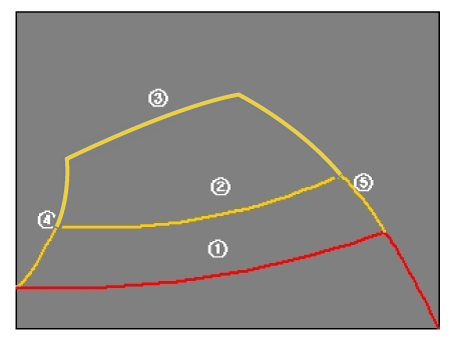
|
SVM System
| 1. |
SVM Video Output
The SVM ECU displays the images from four installed cameras after passing
the distortion correction and image synthesis steps and then displays the
steering assist guidelines in analog format.
|
| 2. |
SVM Switch
The signals are input for control in forward display mode when the switch
is ON.
|
| 3. |
Ignition Input
The SVM ECU displays video only on IGN2 ON and limits video output to
SVM OFF when IGN2 is OFF.
In order to check whether the IGN2 is ON, the SVM ECU uses the signals
to the IGN pin or it uses the M-CAN messages routed to the C-CAN from the
IGPM (Gateway).
|
| 4. |
Switch Indicator Output
The SVM ECU outputs the power of the LED on the SVM switch in PWM waveform
to notify the driver whether or not the SVM switch is pressed.
|
| 5. |
Chassis CAN Input (C-CAN)
The SVM ECU receives the vehicle status data through the C-CAN and determines
whether or not to perform key operations of the SVM.
|
| 6. |
Multimedia CAN Input / Output
The related information is processed after receiving M-CAN signals routed
from the ICU to the C-CAN.
The routed M-CAN signals are exchanged for data transmission and reception
as follows:
|
Repair procedures
Tolerance Compensation
Tolerance compensation compensates for the error margins of surround view video
that occur due to the installation tolerance when the four cameras that comprise
the SVM system are installed.
Tolerance compensation must be carried out when the following actions are performed:
| – |
When removing and installing a wide camera.
|
| – |
When conducting a body task such as the trunk task that causes the focus
of the wide camera to change.
|
| – |
When replacing the door mirror with a wide camera.
|
| – |
When replacing the surround view monitoring unit.
|
Tolerance Compensation
Environments
The Procedure of Manual
Tolerance Compensation
| 1. |
Prepare in advance as below.
| – |
Confirm that the car hood, trunk and doors are closed.
|
| – |
Close the door after getting in on the driver side.
|
| – |
Switch the ignition to "IGN".
|
| – |
Unfold all side mirrors.
|
| – |
Check the flashing state of LED indicator lamp in the SVM switch.
|
| – |
During the advance preparation, do not install exhaust inhaler
or other equipment that may block the view of rearview cameras.
|
| – |
Also, as exhaust fume may block the rearview image, blow off
the smoke by using a fan before performing tolerance compensation
with IGN ON.
|
| – |
Engage foot brake or electronic parking brake (EPB) to hold vehicle
in place.
|
|
| 2. |
Before entering tolerance compensation mode, to check normal operation
of SVM ECU and cameras, perform the following.
| – |
Check that initial setting screen of SVM is displayed. (Front
view image + surround view image when shifted to N)
|
| – |
Check that front, rear, left and right images of surround view
monitor are properly displayed.
|
| – |
If images are properly displayed, enter tolerance compensation
mode. Otherwise, if images are abnormally displayed or are not displayed,
replace relevant part.
|
|
| 3. |
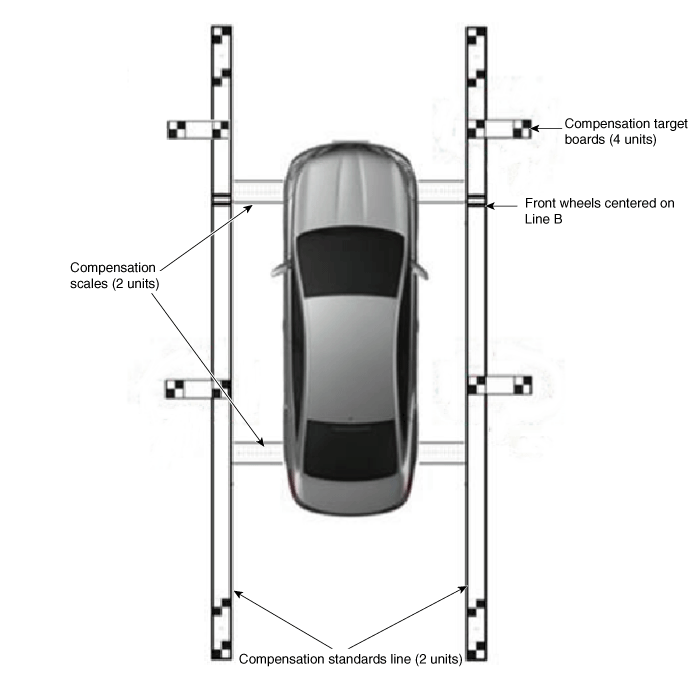
Install two compensation scales, two compensation reference line boards,
and four compensation target boards around the vehicle by referring to the
manual provided with the tools.
| •
|
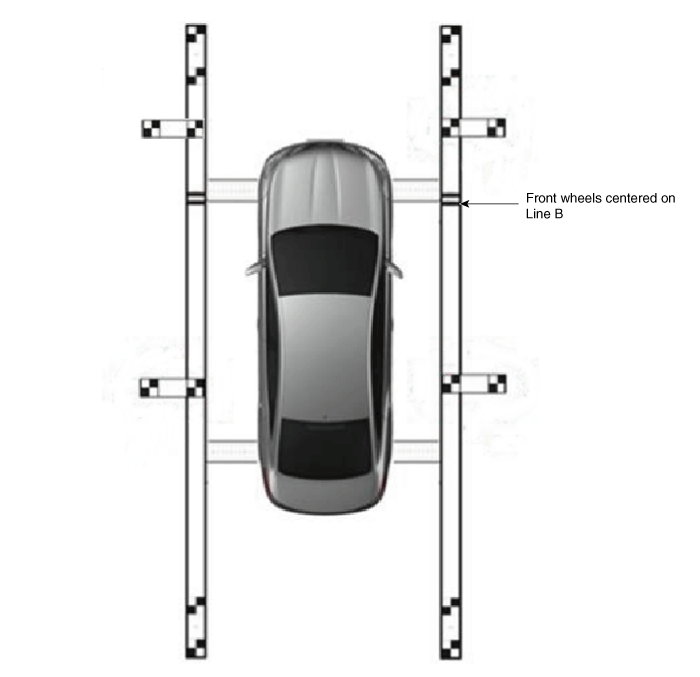
Align centers of front wheels to "B-type" on the compensation
reference line board.
|
| •
|
Accurately set the location (distance/angle) of the center
of white and black compensation board as this is the reference
point.
|
| •
|
Front/rear and left/right alignment error margin should
be below 3 cm.
|
| •
|
Rotation error margin when aligning vehicle should be
within 1° to left/right.
|
|
|
| 4. |
Maintain ignition "ON" with vehicle stopped, check that the gear is in
P, and engage parking brake even on flat ground.
|
| 5. |
Perform work with SVM switched "ON".
|
| 6. |
Connect the KDS to vehicle.
|
| 7. |
Select vehicle model and system.
|
| 8. |
Enter additional function in KDS.
|
| 9. |
Perform SVM manual tolerance compensation as shown on KDS diagnostic
device.
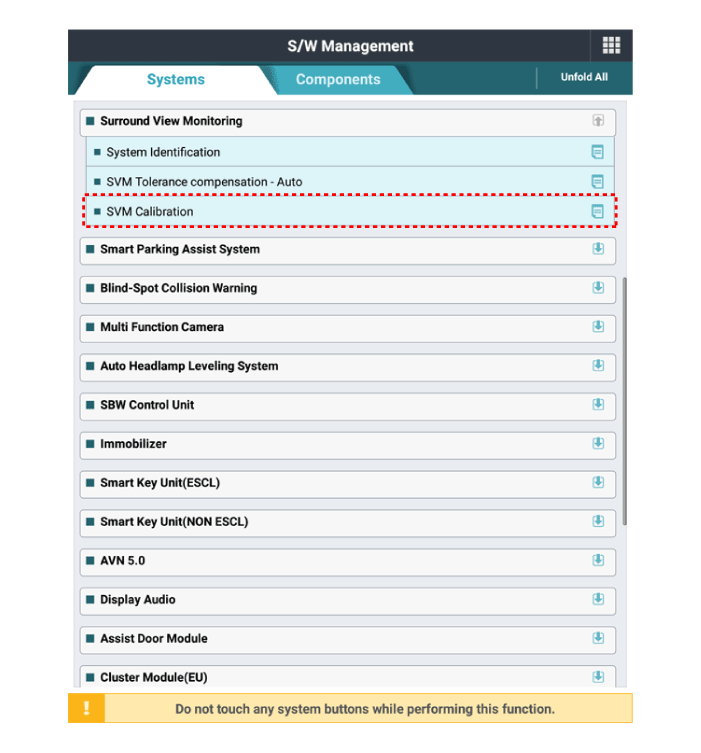
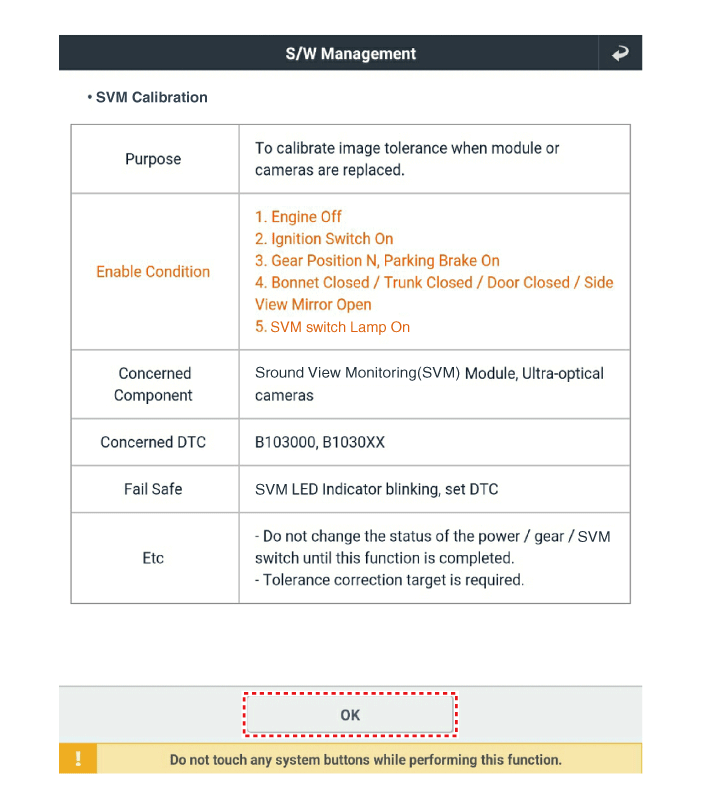
|
When "SVM tolerance compensation - Manual" is clicked on the
KDS diagnostic device screen, the SVM switch indicator lamp will
flash.
|
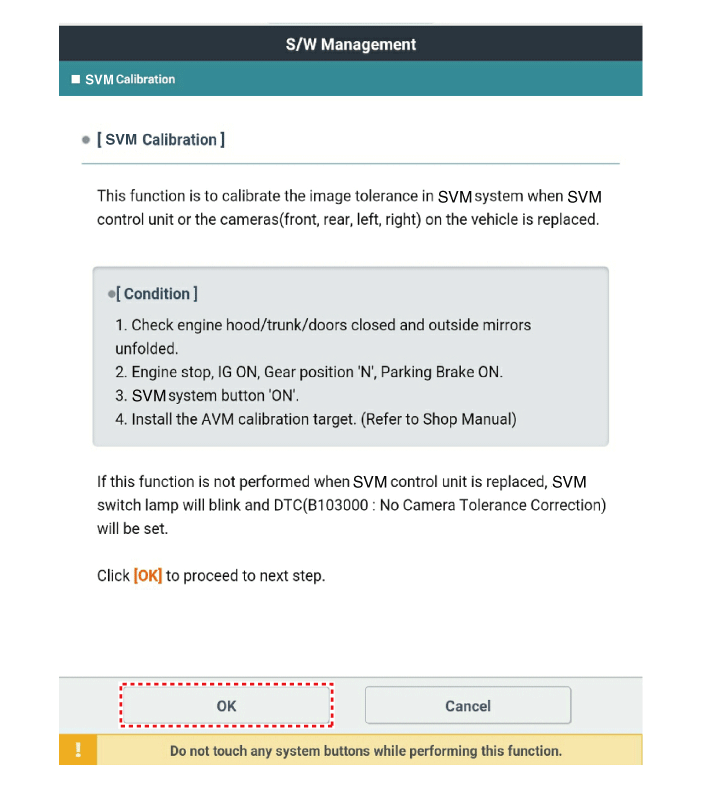
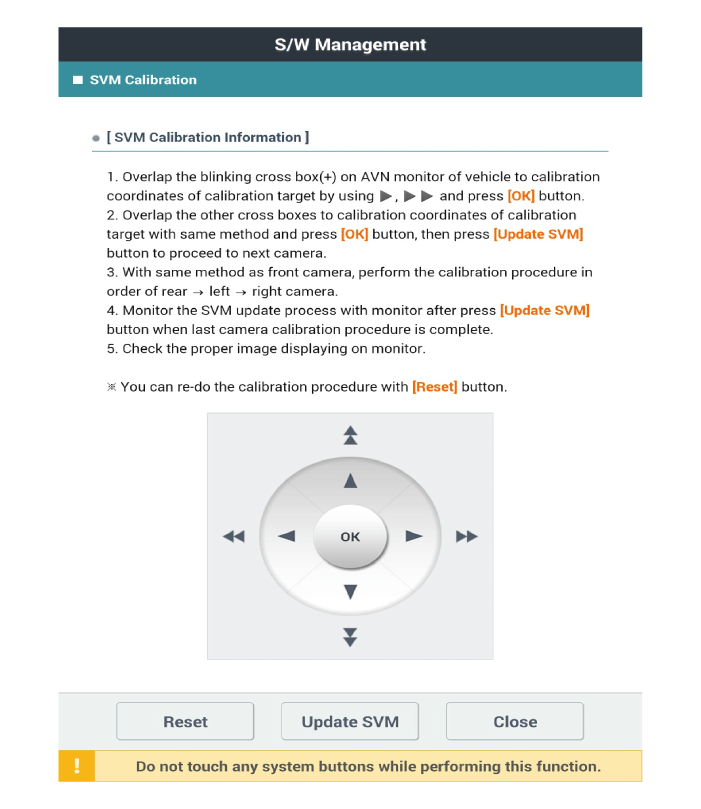
| •
|
Before matching calibration points: "+" green light flashes
|
| •
|
When clicking [OK] after matching calibration points:
"+" red light ON
|
| •
|
Match four frontal calibration points, and then perform
calibration in the order from rear → left → right.

|
|
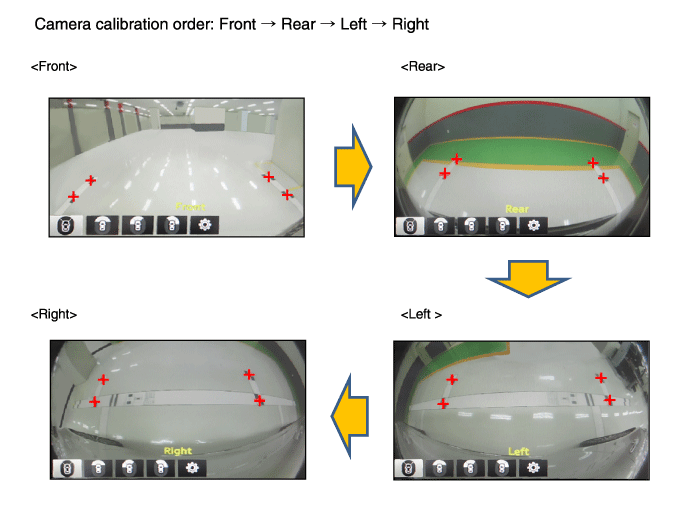
|
| 10. |
To confirm completion of calibration, check the vehicle and calibration
line on AVN monitor and click [OK].
If calibration has not been properly performed, click [Cancel] and reenter
calibration points.
|
Components and components location
Components Location
1. Rear view camera
2. Display audio/AVN head unit
3. Steering angle sensor
Description a ...
Schematic diagrams
Connector and Terminal function
Repair procedures
Removal
1.
Disconnect the negative (-) battery terminal.
2.
...
Other information:
With the door lock button
To unlock a door, push the door lock button (1) to the “Unlock” position.
The red mark on the button will be visible.
To lock a door, push the door lock button (1) to the “Lock” position. If
the door is locked properly, the red mark on the door lock bu ...
Components and components location
Components
[General Type]
1. Sunvisor [LH]
2. Sunvisor [RH]
3. Roof trim
[Panorama Sunroof Type]
1. Sunvisor [LH]
2. Sunvisor [RH]
3. Roof trim
...




 Rear View Monitor (RVM)
Rear View Monitor (RVM) Surround View Monitor (SVM) ECU
Surround View Monitor (SVM) ECU













